Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection in Females
A Urinary Tract Infection commonly referred to as UTI is an infection in any part of the urinary tract including kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It happens when bacteria from the skin or rectum enter the urethra and infect the urinary tract. It can be caused by fungus in some cases and virus in a very rare case. The urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the excreting end of the body. Since the urethra is shorter in women than in men, UTI is 30 times more likely to happen in adult females than in males. If you feel any discomfort while peeing consult urologists in Bangalore without delay. Most symptoms of UTI are common in men and women.
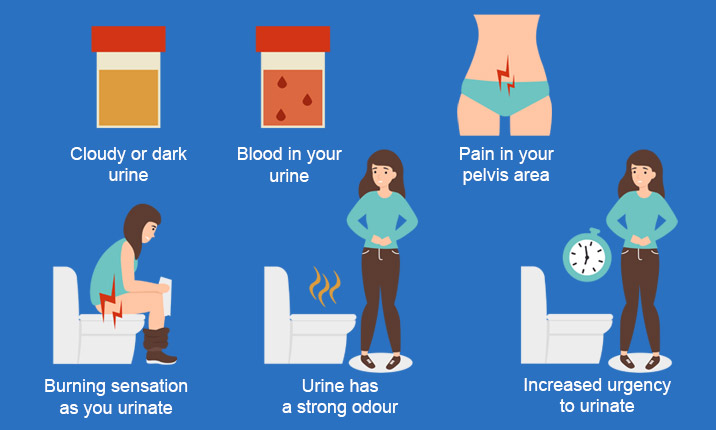
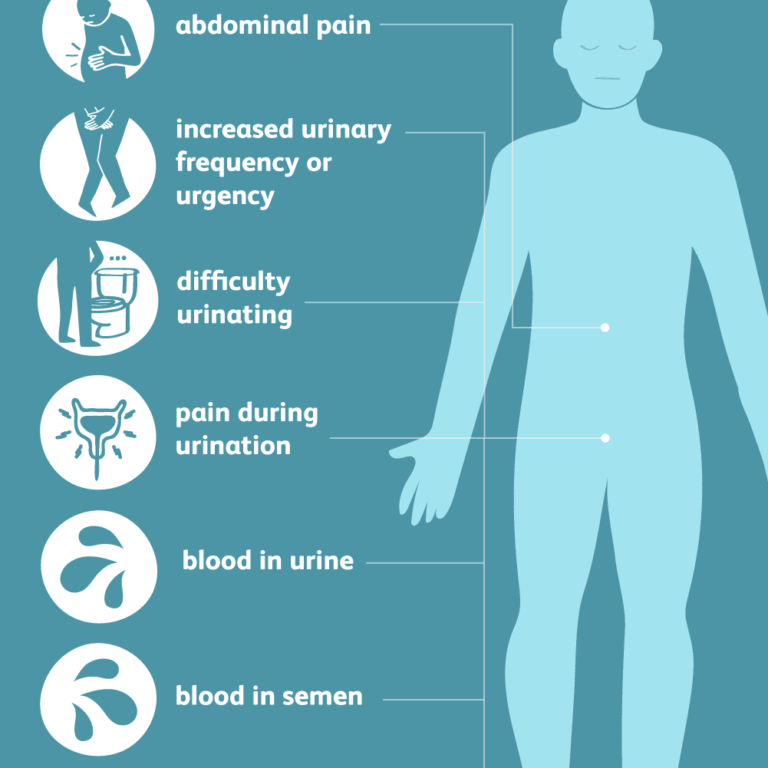
Symptoms of UTI in women include:
A strong and frequent urge to urinate, but not necessarily passing a good amount. Pain, burning or stinging sensation while peeing. Peeing more often during the night than usual. Pee may look cloudy. The presence of blood in urine may lead to red, pink, or cola colour. Odor in urine. Lower abdominal or Pelvic pain around the area of the pubic bone. Pain in the back just under the ribs. Having a fever, feeling hot, or feeling chills. Having a temperature less than 96.8. About 1 to 5 percent of women experience asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB), which is UTI with no symptoms.
In a few conditions women are at more risk of UTI :
Sexual activities can move UTI carrying germs from the vagina to the urethra.
Using a diaphragm with spermicides to prevent pregnancy can kill good bacteria that prevent UTI.
Pregnancy hormones may sometimes change the bacteria in the urinary tract.
Pregnant women sometimes are not able to urinate completely, because the womb sits on the top of the bladder.
Residue can lead to UTI-carrying bacteria.
Loss of estrogen after menopause can lead to dry and thin vaginal tissue which can make an environment for UTI causing bacteria. Diabetes lowers the strength of the immune system, damaging nerves which can make it hard to empty the bladder. Kidney stones can block the flow of urine, leading to UTI. Sometimes during surgery catheters are placed to drain urine when one can’t pass urine on their own. This can also lead to UTI.
Diagnosing UTI
Contact a urologist in Bangalore, if you suspect you have symptoms of UTI. Doctors require a “clean-catch” sample, which is taken in the middle of the urinary stream to avoid bacteria from the skin that can contaminate the sample. Your doctor or lab member will explain how to get a clean catch. If a large number of white blood cells are found, infection is there, later a urine culture is done to check for bacteria, fungus, or virus. Detecting a virus is a rare case, but in people with weaker immune systems or cases with organ transplants viruses can be a cause for UTI.
Treatment of UTI
Depending on the cause, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics. You may feel better in a day or two. But make sure you complete your course.
What happens when UTI is not treated.
The infection can spread to the kidney and other parts of the urinary tract, damaging it, if UTI is not treated on time.
It is more difficult to treat upper tract infection, so it’s always easier and better to treat in the initial stage. If you have recurrent UTIs, knowledgeable urologists in Bangalore may also ask for a few more tests like ultrasound, IVP, cystoscopy or CT scan to get a more detailed idea. Sometimes infection gets to the bloodstream, which can be life-threatening. But this is a rare case
Prevention of UTI
- Drinking fluids (water, milk, fruit juices) is very essential to reduce the chances of UTI. So stay hydrated.
- Avoid fizzy, caffeinated, and alcoholic drinks.
- Eat green vegetables, fruits, and salads that contain higher levels of water.
- Always wash your hands after going to the toilet, before and after cooking and eating.
- Change your pads and tampons regularly.
- Do not use scented wipes or soaps while cleaning between your legs. Use cotton undergarments.
- Always pee after having sex.
- Always clean from front to back.
It’s very important that you follow the directions given by your urologist and complete the course of medicine and supplements prescribed. There’s a different course of treatment for different patients, so follow only what is suggested to you.